

Low-E glass is Low emissivity coated glass which adopts vacuum magnetic control sputtering technology to coat the glass with layers of silver or tin or other metal compounds. The liquid metals or metal powder were directly sprayed onto thermal glass and adhered to its surface at the stage of glass cooling. It is classified into online and Offline Low-E according to its processing technique, the former with single variety and is a hard coating which can be guaranteed for 30years, the latter versatile in color and transmittance, is soft coating but weak in adhesion and can’t be preserved in bareness.

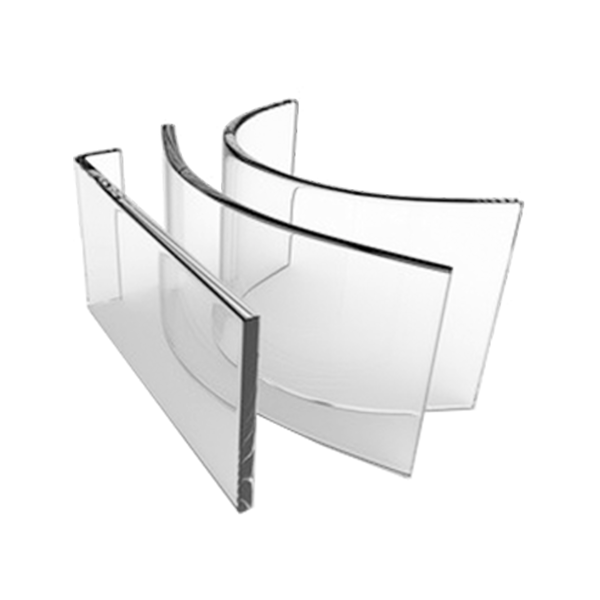
Toughened glass is treated to be far more resistant to breakage than simple annealed glass, and to break in a more predictable way when it does break, thus providing a major safety advantage in almost all of its applications. Toughened glass is made from annealed glass treated with a thermal tempering process. A sheet of annealed glass is heated to above its “annealing point” of 600 °C; its surfaces are then rapidly cooled while the inner portion of the glass remains hotter. The different cooling rates between the surface and the inside of the glass produce different physical properties, resulting in compressive stresses in the surface balanced by tensile stresses in the body of the glass. These counteracting stresses give toughened glass its increased mechanical resistance to breakage, and are also, when it does break, what cause it to produce regular, small, typically square fragments rather than long, dangerous shards that are far more likely to lead to injuries. Toughened glass also has increased resistance to breakage as a result of stresses caused by different temperatures within a pane.


Laminated glass is a kind of safety glass and is hard to break. The glass may be retained in its frame even if being broken. Laminated glass is made of two or more layers of glass with one or more “interlayers” of polymeric material bonded between the glass layers. Poly Vinyl Butyral (PVB) and SentryGlas Plus (SGP) laminated glass is produced using heat and pressure to sandwich a thin layer of PVB or SGP between layers of glass. On occasion, other polymers such as Ethyl Vinyl Acetate (EVA) or Polyurethane (PU) is used. Laminated glass offers many advantages. Safety and security is the best-known of these — rather than shattering on impact, laminated glass is held together by the interlayer, reducing the safety hazard associated with shattered glass fragments, as well as, to some degree, the security risks associated with easy penetration. But the interlayer also provides a way to apply several other technologies and benefits, such as coloring, sound dampening, resistance to fire, ultraviolet filtering, and other technologies that can be embedded in or with the interlayer.

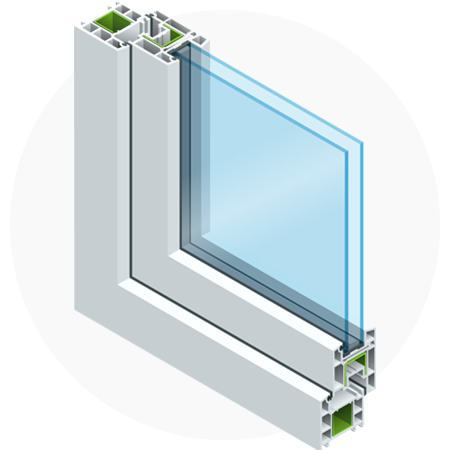
Insulating glass (IG) consists of two or more glass window panes separated by a vacuum or gas-filled(Air,Argon) space to increase a window's thermal performance by reducing the heat gain or loss. Insulated glass units go by different names “double glazing” or “double-pane glass windows.” As a unit since most of the parts are dependent on another for proper performance. Unlike single-pane glass, Insulating glass units are sealed with a primary seal and a secondary seal of silicone. Insulating units are designed to absorb stress on the unit caused by thermal expansion and pressure, provide a barrier to water and moisture infiltration, provide a gas-tight seal to prevent loss of any specialty gas fill and create a barrier that reduces condensation.